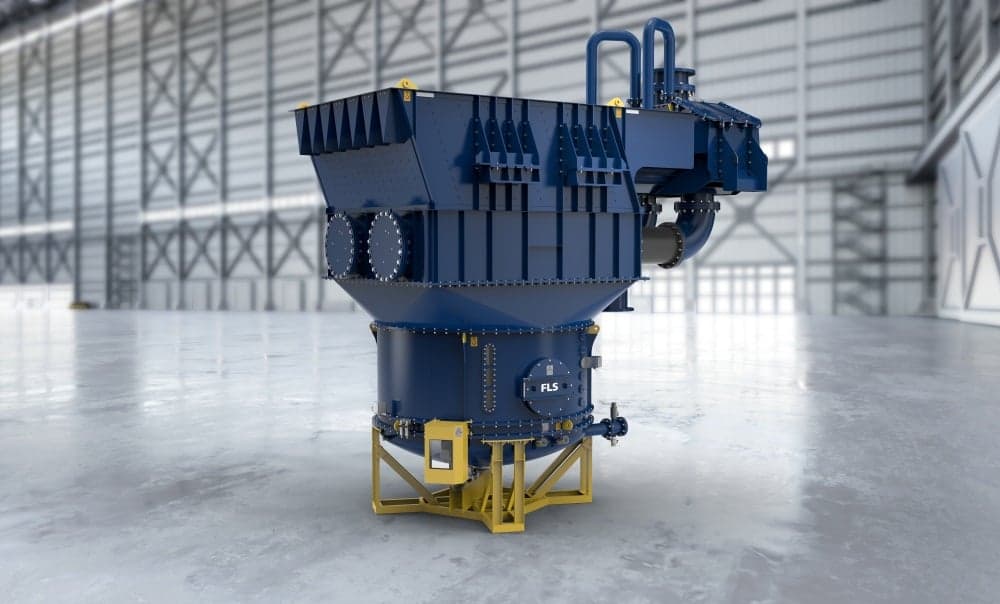
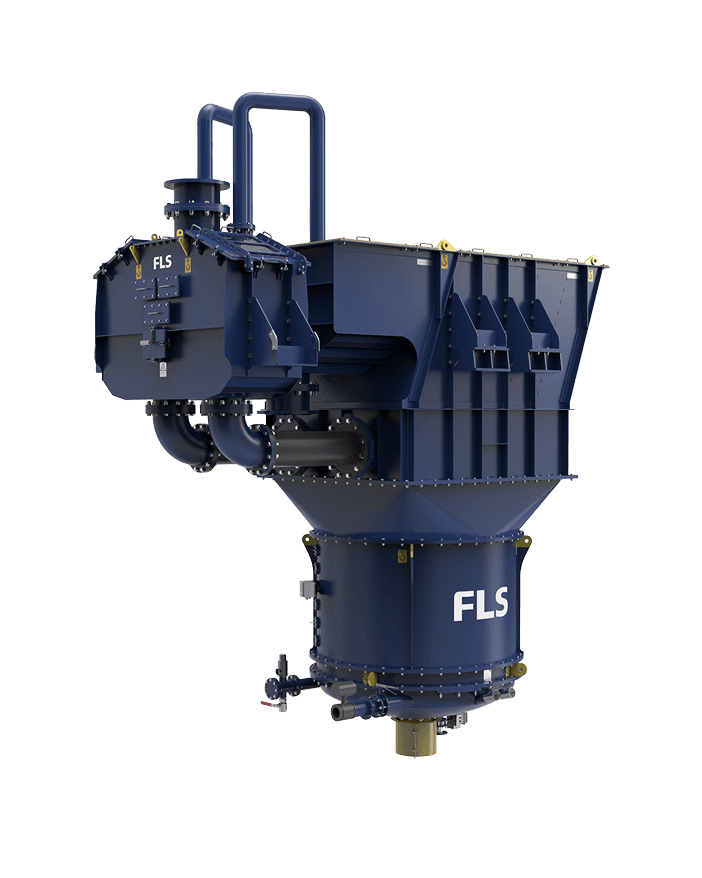
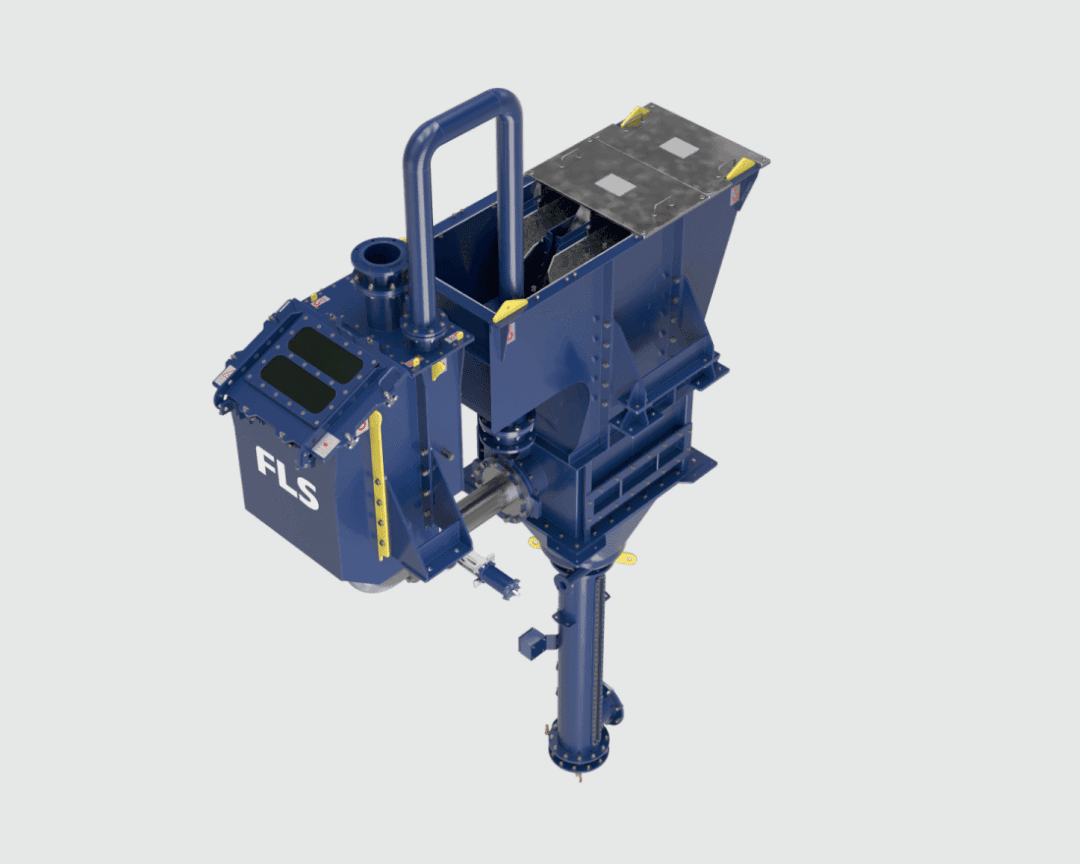
Maintenance & Service of our REFLUX classifiers
Backed by laboratory and pilot-scale testing, we configure our REFLUX Classifier and GradePro Classifier to fit your specific application needs. We have also designed them for ease of transport, site assembly, and installation, reducing set-up time and costs. Our comprehensive aftermarket support includes troubleshooting and optimisation, maintenance support, and spare and wear parts supply.